 Salt Creek is a powerful and riveting account of a family struggling to make a living in the harsh environment of coastal South Australia, depicting the pioneering patriarchal entrepreneur and his devoted but long-suffering wife, and the children that will grow up with both an attachment to the place and an instinct to escape it. This story gets inside you and makes you feel the struggle and the dilemma, and wish that it could have been different.
Salt Creek is a powerful and riveting account of a family struggling to make a living in the harsh environment of coastal South Australia, depicting the pioneering patriarchal entrepreneur and his devoted but long-suffering wife, and the children that will grow up with both an attachment to the place and an instinct to escape it. This story gets inside you and makes you feel the struggle and the dilemma, and wish that it could have been different.
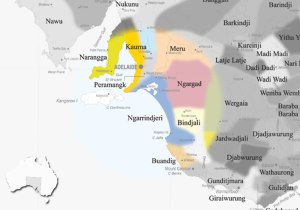
We meet Hester Finch, in Chichester, England in 1874 where she lives as a widow with her son Joss, in the house where her mother spent her childhood, remembered from the stories her mother used to tell, in a place so far from this new reality, of that life in Salt Creek, South Australia.
Hester takes us back to her childhood in the Coorong, narrating the family story throughout the period she lived with them at Salt Creek from 1855 to 1862. Her father was an entrepreneurial businessman, who could never settle to one thing, without always having his eye on the next great idea, the thing that was going to make him rich, a success. For a while the family had lived in Adelaide, while he ran a successful dairying business, but not content to stick with that he would borrow against the things that seemed solid to invest in the next thing. He’d bought land at Salt Creek, but the sheep he’d hoped to farm were lost at sea while being transported, causing the entire family to be uprooted as the family home required selling to pay the debts.
The family find themselves leaving their grandparents, friends and familiar town environment behind to live on an isolated peninsula in rural South Australia. They must rely on each for company, schooling and help their parents out to run the farm and household.
Hester’s mother becomes melancholy and withdrawn from the moment she views her future home, requiring Hester to have to step into a more encompassing role than just that of eldest daughter. To add to her woes, their mother whose youngest Mary is only three years old, discovers she is again with child, and the nearest neighbour not company she can bring herself to indulge.
Mrs Robinson was no comfort to her and never would be; she was the measure for Mama of how far she had fallen.
The family discover indigenous Ngarrindjeri people camping not far from their property, and become interested in a boy named Tully, who is able to speak a little English and seems keen to learn more. Slowly he slips into their lives, though without ever letting go of his ways, his disappearances, his unassuming manner, his sharing of old knowledge about which trees can and shouldn’t be cut, which ducks to avoid, much of it disregarded particularly by the two eldest sons and the father as superstitions to be ignored.
“Do you know what that boy told me today? That we shouldn’t have chopped that tree down and then showed me which ones we should use, can you believe it? Didn’t have all the words but did very well making his thoughts known. I told him we would use the wood that we saw fit since it was ours, not his, and did not trouble to conceal my feelings.”
Although the father believes himself to have an enlightened view, that all men are created equal and seen by the Divine as being equal, his beliefs are challenged when it comes to his own family, both in the example he sets for his son (in relation to indigenous women) and the restrictions he places on his daughters (including his desire to use matrimony as business negotiating device).
It is the younger siblings who grow into and live his more open minded view, and who will force to the surface his deep conditioning, which is unable to embrace those beliefs at all. Hester recalls the first day they set eyes on indigenous people and is filled with remorse:
When I think of what they became to us and how long I have been thinking of them I would like to return to that day and stop the dray and shout at our ghostly memories and the natives: ‘I am sorry. I am sorry for what is to come.’
While the older boys rebel by going off to try their luck in the goldfields, the younger sibling Fred stands his ground and resists his fathers efforts to use him as a form of payment, he spends a lot of time drawing plants in his notebook and is fascinated by the work of Charles Darwin.
“Watching Fred, I began to wonder if it was something other than interest and curiosity alone that drove his actions. He was so purposeful in what he did. Self doubt did not occur to him; he was able to look only at the thing, the task before him. I wished that I could do the same. My own self was mysterious to me. Oh, I knew what I did, but other than that I was invisible to myself…I did not know or see the difference that I made, the space I occupied in this world.”
Hester stays and stays, witness to all that occurs, as the challenges of Salt Creek and the rigid attitude of their father begin to wear everyone down. Hester is warned more than once, that she should not hesitate should there be an opportunity for her to escape. Mrs Robinson comments ‘Hard for girls like you’ to Hester and when questioned why, tells her:
I know, my dear, I know. It’s the expectations that hold you back. They’ll kill you in the end, if you’re not careful, suck the life right out of you. Run, I say. Run whenever you should have the chance, don’t spare a glance back or you’ll turn to salt or stone.”
 The arrival of European settlers, their desire to own and restrict land, to create boundaries, while beneficial to their capitalist desires, becomes increasingly detrimental to the way of life of the indigenous people, as they pollute their fresh water access, introduce sickness and disease and contemplate removing their children.
The arrival of European settlers, their desire to own and restrict land, to create boundaries, while beneficial to their capitalist desires, becomes increasingly detrimental to the way of life of the indigenous people, as they pollute their fresh water access, introduce sickness and disease and contemplate removing their children.
Brilliantly conceived and heartbreaking to read, Salt Creek opens itself wide for discussion on the many issues related to the impact of colonial idealism, whether it’s how it affects women and children, how it impacts and impedes the native population, the imposition of solutions by one group on the other, the inherent disrespect and disregard for a different way of life.
I’m interested to read these accounts yet I am repelled by what transpires, knowing there is little possibility for an alternative ending, it is and always be a kind of clash of civilisations, which annihilates the ancient view, and will only accept its input when it has been turned it into a version of itself.
Lucy Treloar speaks of the considerable unease she felt and continues to feel two years on from its initial publication in Australia, at telling the story, which was partly inspired by her ancestors attempt to set up a farm in the Coorong region. Compelled to share the experience and uncomfortable in the role they played. – Lucy Treloar on writing about indigenous Australians
The short video below gives voice to the Ngarrindjeri people and some hope that we might learn something from their more sustainable way of living in harmony with the natural elements around us.
Note: This book was an ARC (Advance Reader Copy) kindly provided by Aardvark Bureau, an imprint of Gallic Books. It is published in the UK in September 2017.



 Khushwant Singh takes the Punjabi farming village of Mano Majra, a small village on the border between India and Pakistan, one of strategic importance to the railway system, and narrates the moment when news of this change arrives and shows how it affects this community.
Khushwant Singh takes the Punjabi farming village of Mano Majra, a small village on the border between India and Pakistan, one of strategic importance to the railway system, and narrates the moment when news of this change arrives and shows how it affects this community. ‘Why, don’t you people want to be free? Do you want to remain slaves all your lives?
‘Why, don’t you people want to be free? Do you want to remain slaves all your lives? The dual narrative follows firstly the journey of a young woman recovering from her role as a volunteer in World War I, who decides in 1921 to leave England and follow in her French grandfather’s footsteps to Cambodia. Afflicted by strange dreams that seem to relate to the area she is visiting, she tries to unravel their mystery and some of the things written in her grandfather’s journals that don’t initially appear to make sense.
The dual narrative follows firstly the journey of a young woman recovering from her role as a volunteer in World War I, who decides in 1921 to leave England and follow in her French grandfather’s footsteps to Cambodia. Afflicted by strange dreams that seem to relate to the area she is visiting, she tries to unravel their mystery and some of the things written in her grandfather’s journals that don’t initially appear to make sense.
 The Last Gods of Indochine was nominated for the The Man Booker Asian Literary Prize, an award that sadly, has also disappeared.
The Last Gods of Indochine was nominated for the The Man Booker Asian Literary Prize, an award that sadly, has also disappeared. Astonishing, a work of art, an interwoven tapestry of stories that weave across the generations to create something so beautiful, so heartfelt, the thing that connects them is so strong, even when it isn’t known by its characters, somehow Yaa Gyasi conveys that to the reader, so that by the end when something quite magical happens, there is a feeling of grieving for all that has passed and of relief that something new has been found.
Astonishing, a work of art, an interwoven tapestry of stories that weave across the generations to create something so beautiful, so heartfelt, the thing that connects them is so strong, even when it isn’t known by its characters, somehow Yaa Gyasi conveys that to the reader, so that by the end when something quite magical happens, there is a feeling of grieving for all that has passed and of relief that something new has been found.



 Island of a Thousand Mirrors similarly evokes the childhoods and family life of two families living in the same house. The house is owned by the matriarch Sylvia Sumethra and her husband The Judge, who are Sinhala people (an Indo-Aryan ethnic group originally from northern India, now native to and forming the majority (75%) of the population of Sri Lanka, mostly Buddhist) and upstairs they rent to an extended Tamil family (a culturally and linguistically distinct ethnic group native to Sri Lanka, mostly Hindu).
Island of a Thousand Mirrors similarly evokes the childhoods and family life of two families living in the same house. The house is owned by the matriarch Sylvia Sumethra and her husband The Judge, who are Sinhala people (an Indo-Aryan ethnic group originally from northern India, now native to and forming the majority (75%) of the population of Sri Lanka, mostly Buddhist) and upstairs they rent to an extended Tamil family (a culturally and linguistically distinct ethnic group native to Sri Lanka, mostly Hindu).






 Jacky Guard takes Betty to New Zealand as his wife and they set up home in a bay that is handy for their whaling activities and where it is easy to trade with the native Maori population. Jacky trades with, though doesn’t trust the Maori Rangatira (chief), Te Rauparaha. He is able to negotiate with him, but fears he may have disrespected some of their taboo beliefs. There are constant challenges to their attempt to settle on this land, each time they return to Sydney, their home and belongings are often burned on their return.
Jacky Guard takes Betty to New Zealand as his wife and they set up home in a bay that is handy for their whaling activities and where it is easy to trade with the native Maori population. Jacky trades with, though doesn’t trust the Maori Rangatira (chief), Te Rauparaha. He is able to negotiate with him, but fears he may have disrespected some of their taboo beliefs. There are constant challenges to their attempt to settle on this land, each time they return to Sydney, their home and belongings are often burned on their return. Elizabeth Parker, the Real Betty Guard
Elizabeth Parker, the Real Betty Guard
 The Ballroom is Anna Hope’s second novel and one inspired in part by a family connection. I review it in full at
The Ballroom is Anna Hope’s second novel and one inspired in part by a family connection. I review it in full at 


 Eowyn Ivey was the author of my favourite book of 2012 and one of my all time favourite reads, her debut novel
Eowyn Ivey was the author of my favourite book of 2012 and one of my all time favourite reads, her debut novel 

 And in a style true to Eowyn Ivey and familiar from her novel
And in a style true to Eowyn Ivey and familiar from her novel 
 It is 1947, in the province of Punjab, which sits between India and Pakistan, an area where Hindu, Sikh, Muslim and others live side by side. Tension is mounting as political events cause rifts between friends and neighbours as many of the Muslim population support the area becoming part of Pakistan and many Hindu fear for their lives, while the same tensions exist among Muslims living in the predominantly Hindu parts of India.
It is 1947, in the province of Punjab, which sits between India and Pakistan, an area where Hindu, Sikh, Muslim and others live side by side. Tension is mounting as political events cause rifts between friends and neighbours as many of the Muslim population support the area becoming part of Pakistan and many Hindu fear for their lives, while the same tensions exist among Muslims living in the predominantly Hindu parts of India. The thing they all fear most, that some desire most happens and Asha’s family leave their past behind and head for Delhi. Firoze helps them to escape and Asha leaves with a secret she has kept from everyone, the future unknown.
The thing they all fear most, that some desire most happens and Asha’s family leave their past behind and head for Delhi. Firoze helps them to escape and Asha leaves with a secret she has kept from everyone, the future unknown.